Источник: Департамент здравоохранения Москвы
Москва внедрила новый сервис искусственного интеллекта (ИИ) для обнаружения переломов плеча на рентгеновских снимках. По словам Юрия Василева, начальника отдела радиологии Департамента здравоохранения Москвы, это 41-я клиническая область, в которой радиологи используют технологии компьютерного зрения.
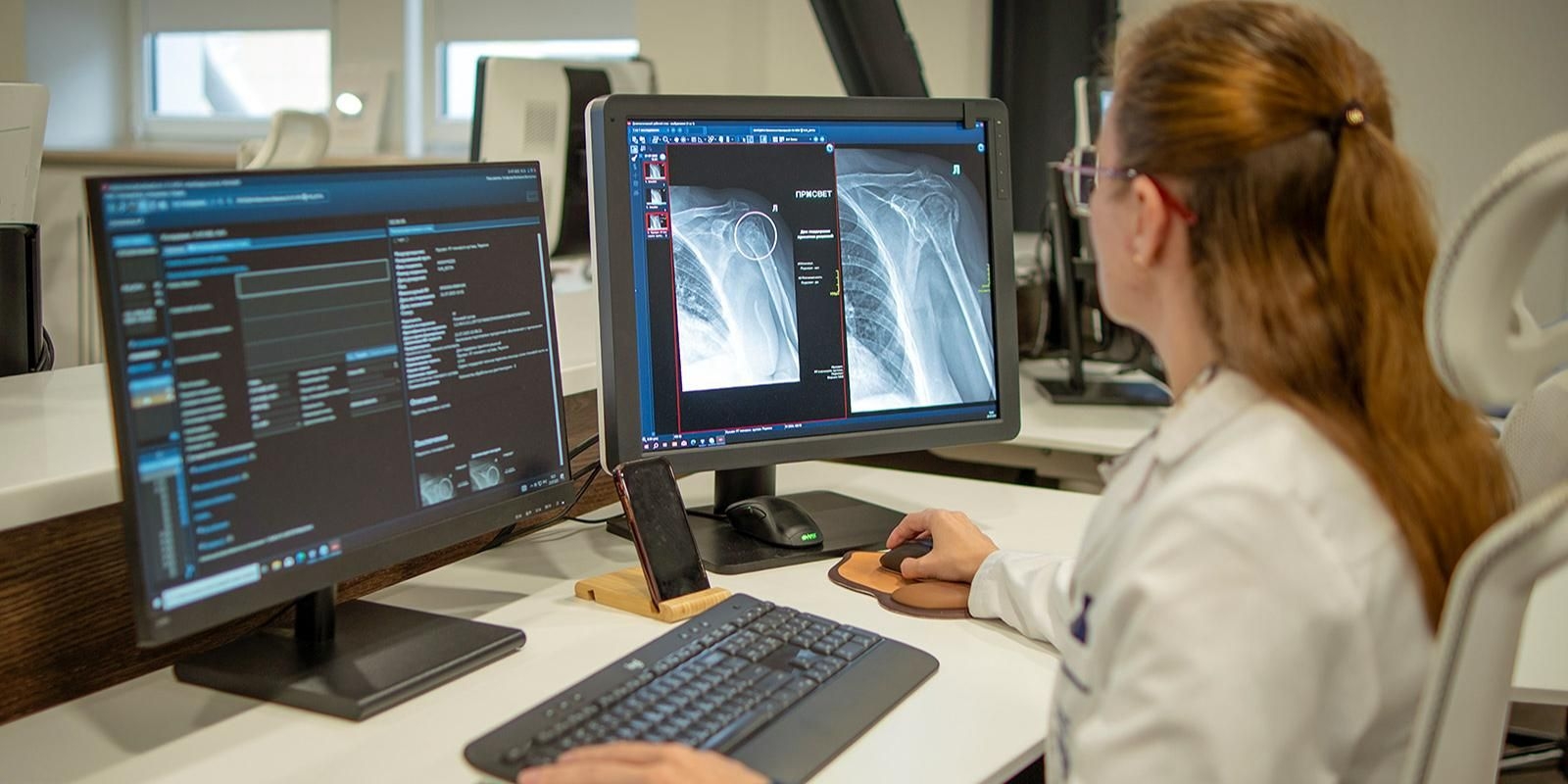
Москва продолжает продвигать интеграцию технологий искусственного интеллекта в практические приложения в сфере здравоохранения. Алгоритм помогает врачам, автоматически выделяя подозрительные области, указывающие на возможные переломы, и выполняя необходимые измерения на снимках. Это ускоряет интерпретацию исследований и повышает точность обнаружения травм. Васильев подчеркнул критическую важность этого сервиса в травматологических центрах, где эффективность и точность диагностики имеют первостепенное значение для своевременного лечения и снижения риска осложнений. Эта интеграция ИИ в травматологию способствует дальнейшему развитию цифровой медицины в Москве, интегрируя сервис в комплексную инфраструктуру нейронных сетей города, которая в настоящее время работает в 41 направлении.
«Плечевой сустав — одна из самых сложных анатомических областей для интерпретации рентгеновских снимков, — отметил Василев. — Даже незначительные отклонения в положении пациента во время обследования могут повлиять на точность визуализации, что требует исключительной внимательности врача. Этот алгоритм искусственного интеллекта действует как дополнительный фильтр, служа надежным вспомогательным инструментом для повышения точности анализа».
«Плечевой сустав является одной из самых сложных анатомических задач для интерпретации рентгеновских снимков», — отметил Василиев. «Даже незначительные отклонения в положении пациента могут повлиять на точность визуализации, что требует исключительной клинической бдительности. Этот алгоритм искусственного интеллекта функционирует как диагностический фильтр, служа надежным вспомогательным инструментом для повышения точности анализа».
Своевременная диагностика переломов имеет решающее значение для определения тактики лечения. Задержки увеличивают риск осложнений, включая неправильное сращение костей, хроническую боль и ограниченную подвижность. Внедрение ИИ минимизирует эти риски, позволяя начать лечение на более ранней стадии.
В рамках пятилетнего эксперимента по компьютерному зрению в Москве в сферу здравоохранения интегрировано более 200 ИИ-сервисов, участвующих в проекте. Около 100 алгоритмов интегрировано в медицинскую информационную систему города, около 50 из них в настоящее время анализируют медицинские изображения в режиме реального времени.
Проект возглавляет Московский комплекс социального развития на базе Центра диагностики и телемедицины Департамента здравоохранения Москвы в сотрудничестве с Департаментом информационных технологий города. Он соответствует целям Стратегии развития медицины в Москве до 2030 года, направленной на улучшение качества и доступности медицинской помощи для жителей.
